In today’s data-driven world, businesses are constantly seeking more effective ways to understand and engage with their customers. The sheer volume of data generated across various touchpoints can be overwhelming, making it challenging to create personalized experiences and drive meaningful interactions. Enter the Customer Data Platform (CDP), a sophisticated solution designed to centralize, unify, and activate customer data from multiple sources. This article provides a deep dive into the world of CDPs, exploring their core functionalities, benefits, and how they are revolutionizing modern data management practices for businesses of all sizes.
This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify Customer Data Platforms and equip you with the knowledge to evaluate whether a CDP is the right investment for your organization. We will explore the key components of a CDP, including data ingestion, identity resolution, segmentation, and activation. Furthermore, we will delve into the differences between CDPs and other related technologies like CRMs and DMPs, highlighting the unique value proposition of a well-implemented CDP in enhancing customer engagement, improving marketing ROI, and driving overall business growth.
Defining Customer Data Platform (CDP): What is it?
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a packaged software that creates a persistent, unified customer database accessible to other systems. This data is pulled from various sources to build a 360-degree view of the customer.
Essentially, a CDP centralizes customer data from online and offline sources, enabling companies to understand their customers better and deliver personalized experiences. Unlike other data management solutions, a CDP is specifically designed for marketing purposes and is managed by the marketing team.
Here’s a breakdown of the key characteristics:
- Persistent and Unified Data: Data is stored long-term and consolidated into a single view.
- Accessible to Other Systems: Data can be shared with other marketing and business applications.
- Customer-Centric: Focuses on creating a complete profile of individual customers.
Core Capabilities of a Customer Data Platform
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is characterized by a set of core capabilities that distinguish it from other data management tools. These capabilities are crucial for achieving a unified and actionable customer view.
Data Ingestion and Unification
CDPs excel at ingesting data from various sources, both online and offline. This includes first-party data (website interactions, purchase history), second-party data (partner data), and sometimes third-party data. The key is the ability to unify this data into a single, coherent customer profile.
Profile Unification and Identity Resolution
A critical function is identity resolution, which involves matching customer data points across different systems and channels to create a persistent, unified customer profile. This ensures that all interactions are attributed to the correct individual.
Segmentation and Activation
CDPs enable sophisticated segmentation of customer data based on various criteria, such as demographics, behavior, and purchase history. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized experiences. Furthermore, CDPs provide activation capabilities, allowing you to push these segments to other marketing and sales platforms.
The Importance of a Unified Customer View
In today’s competitive landscape, a unified customer view is no longer a luxury but a necessity. It represents a single, coherent, and comprehensive understanding of each individual customer across all touchpoints and channels. This holistic perspective is critical for delivering exceptional customer experiences and driving business growth.
Without a unified view, businesses operate with fragmented data, leading to inconsistent messaging, irrelevant offers, and ultimately, a diminished customer experience. Siloed data prevents a complete understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and needs.
A unified customer view enables personalized interactions, proactive customer service, and targeted marketing campaigns. By consolidating data from various sources, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer journeys, identify opportunities for improvement, and build stronger, more meaningful relationships.
CDP vs. CRM: Key Differences and Overlaps
While both Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems deal with customer data, they serve distinct purposes. The primary difference lies in the *type* of data they manage and *how* that data is used.
A CRM is primarily focused on managing direct interactions with customers, such as sales activities, customer service inquiries, and marketing campaigns. It typically stores data entered directly by sales or service representatives. Its purpose is to improve sales processes and customer service.
A CDP, on the other hand, focuses on collecting and unifying all types of customer data from various sources, online and offline. This includes behavioral data, transactional data, and demographic data. The primary purpose of a CDP is to create a unified customer profile that can be used for a wide range of marketing and analytics activities.
In essence, CRMs are interaction-focused, while CDPs are data-focused. Although there is overlap, particularly in contact information, they are not interchangeable.
Benefits of Implementing a CDP for Customer Engagement
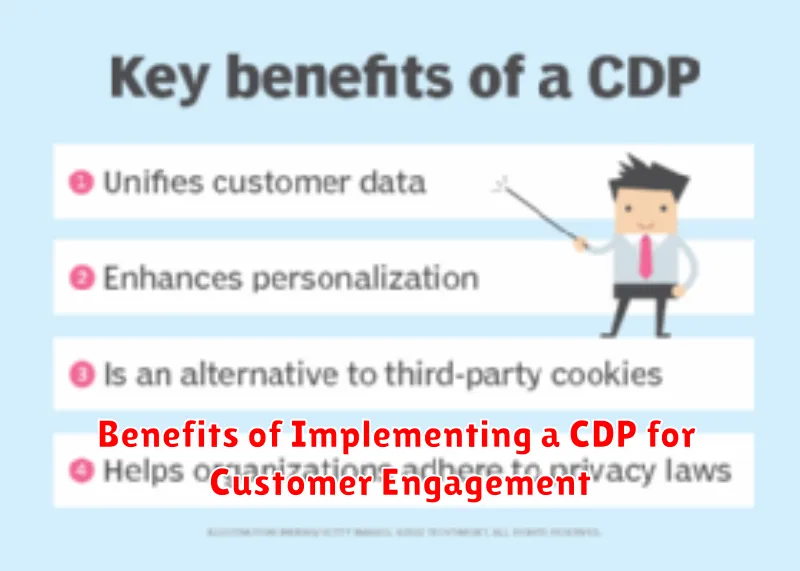
Implementing a Customer Data Platform (CDP) offers numerous benefits for enhancing customer engagement. A primary advantage is the ability to centralize customer data from various sources, providing a single, unified view of each customer. This comprehensive understanding enables businesses to create more personalized and relevant interactions.
Specifically, with a CDP, marketing teams can:
- Improve customer segmentation for targeted campaigns.
- Deliver consistent messaging across all channels.
- Enhance customer experience by providing tailored recommendations and support.
- Increase customer lifetime value through improved retention and loyalty.
Ultimately, a CDP empowers organizations to move beyond generic marketing and engage customers on a more individualized and meaningful level, leading to improved customer satisfaction and business outcomes.
How a CDP Enhances Personalization and Marketing Automation
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) significantly enhances personalization and marketing automation efforts by providing a single, unified view of the customer. This comprehensive profile enables marketers to deliver more relevant and timely messages across various channels.
With a CDP, marketing automation systems can leverage richer, more accurate customer data. This allows for the creation of highly targeted campaigns based on specific behaviors, preferences, and purchase histories. Segmentation becomes more sophisticated, leading to improved engagement and conversion rates.
Here’s how a CDP enables smarter personalization and automation:
- Improved Segmentation: Create granular customer segments based on a wealth of data.
- Personalized Content Delivery: Deliver tailored content based on individual customer profiles.
- Triggered Campaigns: Automate personalized messages based on specific customer actions.
- Optimized Channel Selection: Choose the optimal channel for each customer based on their preferences.
Data Integration and Management within a CDP
A core function of a Customer Data Platform (CDP) is its ability to integrate data from various sources into a unified customer profile. This involves connecting online and offline data, including transactional, behavioral, and demographic information.
Data integration within a CDP typically involves the following steps:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from sources such as websites, apps, CRM systems, email marketing platforms, social media, and point-of-sale systems.
- Data Transformation: Converting data into a consistent format for accurate analysis.
- Identity Resolution: Matching and merging customer data from different sources to create a single customer view.
- Data Storage: Securely storing the unified customer data in a centralized repository.
Effective data management within a CDP ensures data quality, compliance, and accessibility for various business functions. It also involves implementing data governance policies to maintain data integrity and security.
CDP Use Cases: Real-World Examples
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are versatile tools with applications across various industries. Below are some real-world examples demonstrating their value.
Retail: Personalized Shopping Experiences
A retail company uses a CDP to unify customer data from online and offline channels. This enables personalized product recommendations, targeted promotions, and consistent brand messaging across all touchpoints, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.
Financial Services: Enhanced Customer Service
A bank integrates customer data into a CDP to provide a 360-degree view of each customer’s financial activities. This empowers customer service representatives to offer more personalized and efficient support, resolving issues faster and improving customer satisfaction.
Healthcare: Improved Patient Engagement
A healthcare provider uses a CDP to consolidate patient data from various sources, including electronic health records and wearable devices. This facilitates proactive outreach, personalized health recommendations, and improved patient adherence to treatment plans.
E-commerce: Optimizing Marketing Campaigns
An e-commerce business leverages a CDP to track customer behavior across its website and mobile app. This data is used to optimize marketing campaigns, target specific customer segments with relevant ads, and personalize the shopping experience, resulting in higher conversion rates.
Selecting the Right CDP for Your Organization
Choosing the appropriate Customer Data Platform (CDP) is crucial for maximizing its benefits. The selection process should be aligned with your organization’s specific business goals and technical requirements.
Key Considerations:
- Data Integration Capabilities: Ensure the CDP can seamlessly integrate with your existing data sources, including CRM, marketing automation, and e-commerce platforms.
- Identity Resolution: Evaluate the CDP’s ability to accurately identify and unify customer profiles across different channels.
- Segmentation and Activation: Assess the platform’s segmentation capabilities and its ability to activate data for personalized marketing campaigns.
- Scalability and Performance: Consider the CDP’s ability to handle large volumes of data and its performance under increasing loads.
- Security and Compliance: Verify that the CDP adheres to relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Consider conducting a proof of concept (POC) with a few potential vendors to evaluate their platforms in a real-world scenario before making a final decision.
Future of Customer Data Platforms
The future of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) is poised for significant evolution, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-changing landscape of customer expectations. We can anticipate several key trends shaping this evolution.
Firstly, AI and Machine Learning will be increasingly integrated into CDPs, enabling more sophisticated customer segmentation, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences. This will move beyond basic targeting to create truly individualized customer journeys.
Secondly, a greater emphasis on privacy and data governance is anticipated. CDPs will need to adapt to stricter regulations and provide enhanced transparency and control over customer data, fostering trust and ensuring compliance.
Thirdly, the rise of real-time data ingestion and activation will become paramount. Businesses will demand instant insights and the ability to react dynamically to customer behaviors and preferences, necessitating faster data processing capabilities.
Finally, composable CDP architectures are likely to emerge, offering greater flexibility and customization. This will allow organizations to tailor their CDP solutions to specific needs and integrate seamlessly with other marketing and technology platforms.