In today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape, understanding the impact of marketing investments is crucial for sustained growth. Organizations are constantly seeking effective strategies to optimize their marketing spend and maximize returns. Enter Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), a powerful analytical approach that provides a comprehensive framework for measuring and optimizing the effectiveness of various marketing activities. This article serves as an in-depth overview of MMM, exploring its core principles, benefits, and practical applications for driving data-driven marketing decisions and unlocking significant growth potential.
This comprehensive exploration of Marketing Mix Modeling will delve into the methodologies employed, including statistical modeling techniques used to quantify the impact of each marketing channel on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales, revenue, and brand awareness. We will examine how MMM enables businesses to understand the relative contribution of different marketing elements – including advertising, promotions, pricing, and distribution – thereby facilitating more informed resource allocation and strategic campaign planning. Furthermore, we will address common challenges and best practices for implementing successful MMM initiatives to ensure accurate and actionable insights, contributing to sustainable business growth and a stronger return on marketing investment (ROMI).
What is Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)?
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is a sophisticated statistical analysis technique used to measure the impact of various marketing activities on sales or other key performance indicators (KPIs). It provides a holistic view of marketing effectiveness by quantifying the contribution of each element of the marketing mix, such as advertising, promotions, pricing, and distribution.
Essentially, MMM aims to understand how different marketing channels interact and contribute to overall business performance. By analyzing historical data, MMM helps businesses optimize their marketing spend, forecast future outcomes, and make more informed decisions about resource allocation.
The core output of an MMM analysis is a set of statistical models that estimate the return on investment (ROI) for each marketing activity. This information allows marketers to identify the most effective channels and strategies, and to adjust their plans accordingly for maximum impact.
The Core Components of an Effective MMM
An effective Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) framework comprises several essential components that work synergistically to provide actionable insights. These components ensure the model is comprehensive, accurate, and useful for strategic decision-making.
1. Data Collection and Integration: This involves gathering relevant data from various sources, including sales figures, marketing spend across different channels (TV, digital, print, etc.), pricing data, promotional activities, and external factors like seasonality and economic indicators. The data must be properly cleaned, transformed, and integrated into a unified dataset.
2. Variable Selection: Identifying which variables to include in the model is crucial. This includes both marketing and non-marketing variables that can influence sales. Statistical techniques and domain expertise are used to select the most relevant predictors.
3. Model Building: Choosing the appropriate statistical model (e.g., linear regression, time series models) based on the data characteristics and business objectives. This involves defining the relationships between marketing activities and sales outcomes.
4. Calibration and Validation: Ensuring the model’s accuracy by calibrating it with historical data and validating its performance on unseen data. This helps to prevent overfitting and ensures the model can generalize to future periods.
5. Reporting and Visualization: Communicating the model’s results in a clear and actionable format. This includes creating visualizations, dashboards, and reports that highlight the key drivers of sales and provide recommendations for optimizing marketing spend.
Benefits of Implementing Marketing Mix Modeling
Implementing Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) offers significant advantages for businesses seeking to optimize their marketing investments and drive growth. MMM provides a holistic view of marketing effectiveness, enabling informed decision-making.
Key Benefits:
- Improved Budget Allocation: MMM helps identify the most effective marketing channels, allowing for reallocation of resources to maximize ROI.
- Enhanced Marketing Strategy: By understanding the impact of different marketing activities, companies can refine their overall strategy for better results.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: MMM provides objective, data-driven insights, reducing reliance on intuition or guesswork.
- Optimized Marketing Mix: MMM facilitates the creation of a marketing mix that maximizes impact and minimizes waste.
- Predictive Capabilities: MMM can forecast the potential impact of future marketing campaigns, enabling proactive planning.
In essence, MMM empowers businesses to make smarter, more effective marketing decisions, leading to increased revenue and improved profitability.
MMM vs. Attribution Modeling: Key Differences
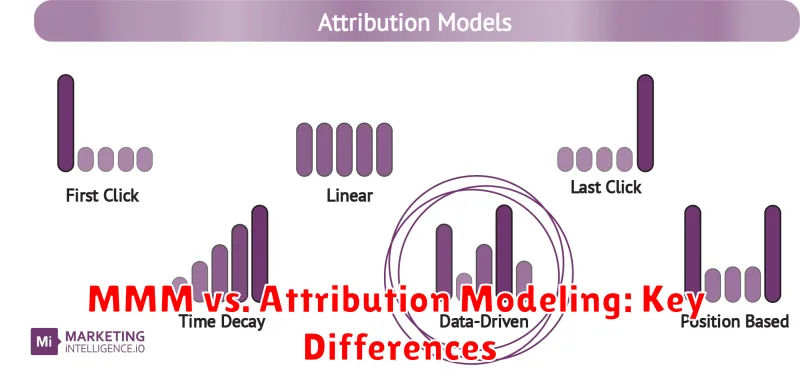
While both Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) and Attribution Modeling aim to understand marketing effectiveness, they differ significantly in their approach and scope. MMM is a top-down approach that analyzes the overall impact of various marketing activities on sales or revenue using statistical techniques like regression analysis. It focuses on the aggregate effect of marketing spend over time, considering factors like seasonality and macroeconomic trends.
In contrast, Attribution Modeling is a bottom-up approach that focuses on identifying the specific touchpoints that led to a conversion or sale. It assigns credit to each touchpoint in the customer journey, allowing marketers to understand which channels and campaigns are most effective at driving conversions. Attribution models typically operate at a more granular level, analyzing individual user interactions and website behavior. It relies heavily on cookies and tracking pixels.
Key Differences Summarized:
- Scope: MMM analyzes aggregate data; Attribution Modeling analyzes individual customer journeys.
- Approach: MMM is top-down; Attribution Modeling is bottom-up.
- Data: MMM uses historical sales and marketing spend data; Attribution Modeling uses clickstream and conversion data.
- Granularity: MMM provides a holistic view; Attribution Modeling provides a detailed view of individual touchpoints.
Data Sources for Marketing Mix Modeling
Effective Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) relies on a diverse and comprehensive set of data sources. The quality and breadth of these sources directly impact the accuracy and reliability of the model’s outputs.
Key data sources include:
- Sales Data: This encompasses historical sales figures, often broken down by product, region, and channel.
- Marketing Spend Data: Detailed information on marketing expenditures across various channels (e.g., TV, digital advertising, print). This includes budgets, actual spend, and campaign specifics.
- Pricing Data: Historical pricing information, including promotions, discounts, and list prices.
- Distribution Data: Information on product distribution channels, including availability, shelf space, and retailer-specific data.
- Economic Data: Macroeconomic indicators such as GDP, inflation, and unemployment rates.
- Competitive Data: Information on competitor activities, including marketing spend, pricing, and product launches.
- Website and Digital Analytics: Data from website analytics platforms (e.g., Google Analytics) providing insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates.
- Social Media Data: Data from social media platforms on brand mentions, engagement, and sentiment.
The integration of these varied data streams is crucial for building a robust and insightful MMM.
Challenges in Building and Maintaining an MMM
Building and maintaining a Marketing Mix Model (MMM) presents several significant challenges. These challenges can impact the accuracy, reliability, and ultimately, the usefulness of the model.
One major hurdle is data availability and quality. MMM relies on comprehensive historical data across various marketing channels. Missing, incomplete, or inaccurate data can skew results and lead to flawed insights. Ensuring data cleanliness and consistency is therefore crucial.
Model complexity and interpretation also pose difficulties. MMMs often involve intricate statistical techniques, requiring specialized expertise to build, validate, and interpret. Communicating findings to stakeholders who may not have a statistical background can be challenging.
Furthermore, external factors and market dynamics can impact model accuracy. Changes in consumer behavior, competitive landscape, or economic conditions can render a model obsolete if not regularly updated and recalibrated. Maintaining model relevance over time necessitates ongoing monitoring and adjustments.
Finally, resource constraints, including budget and personnel, can limit the scope and sophistication of MMM efforts. A robust MMM requires a significant investment in data collection, modeling software, and skilled analysts.
How to Interpret MMM Results
Interpreting Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) results is crucial for making informed decisions about marketing investments. The primary outputs of an MMM are the contribution and Return on Investment (ROI) of each marketing channel.
Contribution represents the percentage of sales attributed to each marketing channel. This allows you to understand which channels are driving the most revenue.
ROI indicates the profitability of each channel. A higher ROI suggests that the channel is generating more revenue for every dollar invested.
Furthermore, MMM provides insights into the effectiveness of marketing spend over time. By examining trends and patterns in the results, you can identify periods where marketing campaigns were particularly successful or underperforming.
Consider the baseline sales. MMM helps to understand the level of sales achieved without any marketing activity. It’s essential to account for factors like seasonality and price effects.
Careful analysis of these metrics enables you to optimize your marketing budget, allocate resources effectively, and improve overall marketing performance.
Advanced Techniques in Marketing Mix Modeling
Beyond the foundational MMM approaches, several advanced techniques can enhance model accuracy and provide deeper insights. These methods address complexities such as non-linear effects, time-varying relationships, and diminishing returns.
Incorporating Bayesian Methods
Bayesian MMM allows for the integration of prior knowledge and uncertainty into the model. This is particularly useful when historical data is limited. Bayesian approaches provide a probability distribution over the model parameters, offering a more robust assessment of marketing effectiveness.
Machine Learning Integration
Machine learning algorithms, such as neural networks and random forests, can capture complex, non-linear relationships between marketing inputs and outcomes. These techniques can improve predictive accuracy but require careful validation to avoid overfitting.
Time Series Analysis
Using time series models like ARIMA or Prophet can help account for seasonality, trends, and autocorrelations in the data, leading to more accurate attribution of marketing impact.
Shape Effects and Saturation Curves
Employing shape effects such as Adstock or Carryover effects can better represent how marketing activities influence consumer behavior over time. Similarly, saturation curves can model the diminishing returns of marketing spend as campaigns reach saturation points.
The Future of Marketing Mix Modeling
The future of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) is poised for significant evolution, driven by technological advancements and the increasing complexity of the marketing landscape. We can anticipate a greater integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance model accuracy and efficiency.
Here’s a glimpse into what we can expect:
- Enhanced Granularity: MMM will delve deeper into granular data, capturing nuances in consumer behavior.
- Real-Time Insights: Expect a shift towards more real-time or near real-time MMM solutions, enabling faster decision-making.
- Improved Integration: Seamless integration with other marketing technologies and data sources will be crucial.
- Advanced Scenario Planning: More sophisticated tools for simulating various marketing scenarios and predicting outcomes.
- Focus on Incrementality: A greater emphasis on measuring the true incremental impact of marketing activities.
The rise of privacy-centric marketing and the decline of third-party cookies will further necessitate the use of MMM as a reliable measurement solution. As data privacy regulations evolve, MMM will adapt by incorporating privacy-preserving techniques. It will solidify its position as a strategic tool for optimizing marketing investments and driving sustainable growth.
Best Practices for Successful MMM Implementation
To ensure the effectiveness of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), adherence to best practices is crucial. These guidelines can maximize the insights derived and the return on investment.
Data Integrity and Quality
Prioritize data quality. Garbage in, garbage out. Ensure all data sources are accurate, consistent, and properly cleaned. Implement rigorous data validation processes to minimize errors and biases.
Clearly Defined Objectives
Establish clear, measurable objectives before initiating the MMM project. Define what you want to achieve with the model (e.g., optimize budget allocation, understand channel effectiveness). This will guide the model development and interpretation of results.
Cross-Functional Collaboration
Foster collaboration between marketing, analytics, and finance teams. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the marketing landscape and facilitates buy-in for model recommendations.
Regular Model Refreshment
MMM is not a one-time project. Regularly refresh the model with new data to account for changes in market dynamics, competitive landscapes, and consumer behavior. A quarterly review is advisable.
Actionable Insights and Implementation
Translate model outputs into actionable insights. Develop a plan to implement the recommendations and track the results. Regularly monitor and adjust strategies based on the model’s performance.