In today’s increasingly complex digital landscape, understanding the customer journey is paramount for marketing success. Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) emerges as a crucial framework for unraveling the intricate web of touchpoints that influence a customer’s purchasing decision. This beginner’s guide will demystify MTA, providing a clear and concise explanation of its principles, benefits, and implementation. From grasping the fundamentals of attribution modeling to selecting the right tools, this resource will equip you with the knowledge to optimize your marketing campaigns and drive ROI.
This guide is designed for individuals with varying levels of marketing experience who seek to enhance their understanding of MTA. Whether you’re a seasoned marketing professional or just beginning your journey, this resource will provide actionable insights and practical strategies for leveraging multi-touch attribution. We will explore the various attribution models available, such as first-touch, last-touch, linear, time-decay, and position-based, helping you determine which model best aligns with your business objectives. By mastering MTA, you can gain a holistic view of your marketing efforts, identify high-performing channels, and make data-driven decisions to maximize your marketing impact.
What is Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) and Why is it Important?
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) is a marketing analytics technique that assigns credit to multiple touchpoints in the customer journey for contributing to a conversion. Unlike single-touch attribution models, which attribute 100% of the credit to a single interaction (either the first or last), MTA acknowledges that customers typically interact with a brand across various channels and devices before making a purchase or completing a desired action.
Why is MTA important? It provides a more holistic and accurate view of marketing effectiveness. By understanding which touchpoints are most influential, marketers can:
- Optimize marketing spend by allocating resources to the most effective channels.
- Improve customer experience by understanding the customer journey and identifying areas for improvement.
- Increase conversion rates by tailoring messaging and offers to specific customer segments.
In essence, MTA helps businesses move beyond guesswork and make data-driven decisions about their marketing strategies, leading to improved ROI and stronger customer relationships.
Understanding Single-Touch vs. Multi-Touch Attribution Models
Attribution modeling is the process of identifying which touchpoints in a customer journey receive credit for a conversion. Understanding the difference between single-touch and multi-touch models is crucial for effective marketing analysis.
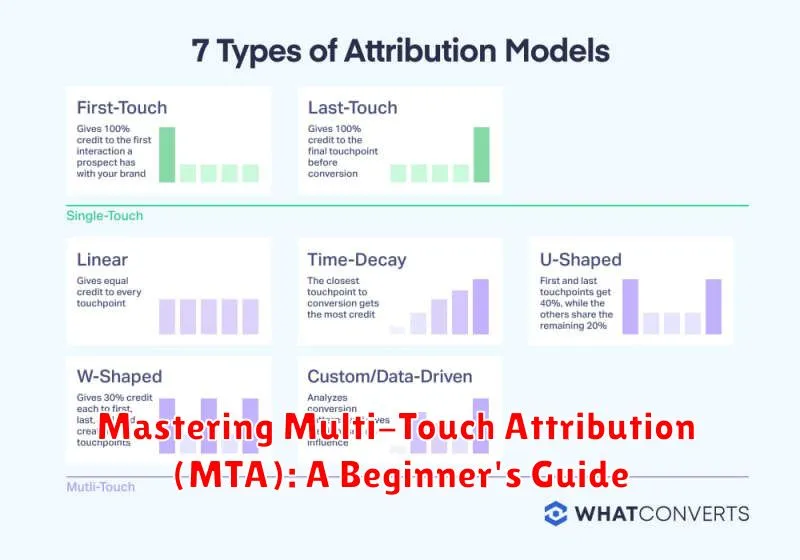
Single-Touch Attribution
Single-touch attribution models assign 100% of the credit for a conversion to a single touchpoint. Common examples include:
- First-Touch Attribution: Credit goes to the very first interaction a customer has with your brand.
- Last-Touch Attribution: Credit goes to the final interaction before the conversion.
While simple to implement, these models provide an incomplete picture of the customer journey, potentially overvaluing or undervaluing specific touchpoints.
Multi-Touch Attribution
Multi-touch attribution models distribute credit across multiple touchpoints that contributed to the conversion. This offers a more holistic view of the customer journey. Examples of these models will be discussed later.
By considering multiple interactions, multi-touch attribution provides a more accurate understanding of marketing effectiveness, leading to better informed optimization decisions.
The Different Types of MTA Models: Linear, Time Decay, U-Shaped, and W-Shaped
Several multi-touch attribution (MTA) models exist, each distributing credit differently across touchpoints in the customer journey. Understanding these models is crucial for selecting the most appropriate one for your business.
Linear Attribution
The linear model gives equal credit to every touchpoint along the conversion path. This is a simple model that is easy to understand and implement, but it may not accurately reflect the true influence of each touchpoint.
Time Decay Attribution
The time decay model assigns more credit to touchpoints that occur closer in time to the conversion. The idea is that touchpoints that are closer to the purchase are more influential.
U-Shaped (Position-Based) Attribution
The U-shaped model, also known as position-based, assigns the most credit to the first and last touchpoints, with the remaining touchpoints receiving a smaller, equal share. This model recognizes the importance of initial awareness and the final conversion.
W-Shaped Attribution
The W-shaped model gives significant credit to the first touch, the lead creation touch, and the opportunity creation touch. The remaining credit is distributed among other touchpoints. It focuses on the key stages of the sales funnel.
Choosing the Right MTA Model for Your Business

Selecting the appropriate Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) model is crucial for accurately evaluating the impact of your marketing efforts. The “right” model depends heavily on your specific business objectives, marketing strategies, and the complexity of your customer journey.
Here are some factors to consider:
- Business Goals: Are you focused on brand awareness, lead generation, or sales conversions? Different models emphasize different touchpoints.
- Customer Journey Length: Shorter, simpler journeys may benefit from simpler models like Linear or U-Shaped. Longer, more complex journeys may require more sophisticated models like Time Decay or W-Shaped.
- Data Availability: Ensure you have sufficient data across all touchpoints to effectively implement and analyze your chosen model.
- Testing and Iteration: Start with a model that aligns with your initial understanding and iteratively test and refine your approach as you gather more data and insights.
Consider starting with a simpler model and gradually transitioning to a more complex one as your understanding of the customer journey deepens and your data matures.
Implementing an MTA Solution: A Technical Overview
Implementing a Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) solution requires a structured approach, encompassing data collection, integration, and analysis. This technical overview provides a high-level understanding of the key steps involved.
Data Collection and Integration
The initial step involves identifying and collecting relevant data from various marketing touchpoints. Common sources include:
- Website analytics: Tracking user behavior on your website.
- CRM systems: Customer relationship management data.
- Advertising platforms: Data from Google Ads, Facebook Ads, etc.
- Email marketing platforms: Tracking email opens, clicks, and conversions.
Data integration typically involves using an ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) process to consolidate data into a centralized data warehouse or MTA platform.
Platform Selection and Configuration
Choosing the right MTA platform is crucial. Consider factors like data integration capabilities, reporting features, and the supported attribution models. Once selected, configure the platform to accurately track and attribute conversions to the relevant touchpoints. Proper tag management is essential for consistent data capture across all channels.
Reporting and Analysis
The final step involves generating reports and analyzing the attribution data. This requires understanding the platform’s reporting capabilities and interpreting the data to identify the most effective marketing channels and touchpoints. Regularly monitor the performance of your MTA model and adjust your marketing strategies accordingly.
Data Sources for Multi-Touch Attribution
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) relies on comprehensive data collection to accurately assign credit to various touchpoints in the customer journey. Identifying and integrating the right data sources is critical for a successful MTA implementation. The quality and breadth of these sources directly impact the insights derived and the effectiveness of marketing optimization efforts.
Key data sources include:
- Website Analytics: Data from platforms like Google Analytics or Adobe Analytics, providing insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversions.
- CRM Systems: Data on leads, customers, and sales activities, offering information on customer interactions and purchase history.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Data on email campaigns, marketing automation workflows, and lead nurturing activities.
- Advertising Platforms: Data from platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn Ads, providing information on ad impressions, clicks, and conversions.
- Social Media Analytics: Data on social media engagement, reach, and conversions.
- Offline Data: Data from brick-and-mortar stores, call centers, and direct mail campaigns.
Integrating these data sources effectively, often through a Data Management Platform (DMP) or a Customer Data Platform (CDP), allows for a holistic view of the customer journey and more accurate attribution modeling.
Challenges and Limitations of MTA
While Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) offers significant advantages, it’s essential to acknowledge its inherent challenges and limitations.
Data Quality and Completeness
The accuracy of MTA heavily relies on the quality and completeness of the underlying data. Incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to skewed attribution and misinformed marketing decisions. Ensuring data integrity across all touchpoints is crucial.
Complexity and Implementation
Implementing and maintaining an MTA solution can be complex, requiring technical expertise and resources. The process involves integrating data from various sources, configuring the model, and continuously monitoring its performance. This complexity can be a barrier for smaller businesses or those with limited resources.
“Black Box” Concerns
Some MTA models, particularly those powered by advanced algorithms, can be perceived as “black boxes.” Understanding how specific touchpoints are weighted and attributed can be challenging, potentially hindering trust and transparency.
Privacy Concerns
Collecting and using user data for MTA raises privacy concerns. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is paramount. Anonymization and data aggregation techniques are essential to protect user privacy while still leveraging MTA insights.
Best Practices for Multi-Touch Attribution
Implementing Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) effectively requires adherence to several best practices to ensure accurate insights and optimized marketing strategies. These practices encompass data management, model selection, and ongoing analysis.
Data Integrity and Management: Prioritize data quality by implementing robust tracking mechanisms and regularly auditing data for discrepancies. Ensure consistent data collection across all touchpoints.
Model Selection and Customization: Carefully select an MTA model that aligns with your business goals and customer journey. Consider customizing the model to account for unique aspects of your marketing ecosystem.
Regular Analysis and Iteration: Continuously analyze attribution data to identify trends and patterns. Use these insights to refine marketing campaigns and improve ROI. Be prepared to iterate on your chosen model and data collection methods as needed. This includes revisiting channel weighting and data integration processes.
Using MTA to Optimize Your Marketing Campaigns
Multi-Touch Attribution (MTA) provides invaluable insights into the customer journey, allowing marketers to refine their strategies and maximize ROI. By understanding which touchpoints are most influential in driving conversions, businesses can strategically allocate resources to the most effective channels and campaigns.
Here’s how you can leverage MTA to optimize your marketing campaigns:
- Identify High-Performing Touchpoints: Discover which interactions have the greatest impact on conversions.
- Optimize Channel Spend: Shift budget from underperforming channels to those that are driving results.
- Personalize Customer Journeys: Tailor messaging and content based on individual customer interactions and preferences.
- Improve Campaign Targeting: Refine audience targeting to reach the most receptive prospects.
- A/B Test Different Scenarios: Experiment with different touchpoint combinations and messaging to identify the most effective paths to conversion.
By using MTA to gain a deeper understanding of the customer journey, marketers can create more effective and efficient campaigns that deliver a greater return on investment.
The Future of Multi-Touch Attribution: AI and Machine Learning

The future of multi-touch attribution (MTA) is inextricably linked with advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These technologies offer the potential to overcome many of the limitations currently associated with traditional MTA models.
AI and ML can enhance MTA in several key areas:
- Advanced Pattern Recognition: ML algorithms can identify subtle patterns and correlations in customer data that would be impossible for humans or rule-based systems to detect.
- Predictive Attribution: AI can predict the impact of different touchpoints on conversion, allowing marketers to optimize campaigns proactively.
- Personalized Attribution: ML can tailor attribution models to individual customer journeys, providing a more accurate understanding of the channels that influence each customer.
- Automated Model Optimization: AI can automatically adjust attribution models based on real-time data, ensuring they remain accurate and effective over time.
As AI and ML continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly important role in helping marketers understand and optimize the customer journey. Expect to see more sophisticated MTA solutions that leverage these technologies to deliver greater accuracy, efficiency, and actionable insights.