In today’s digital advertising landscape, consumers are increasingly adept at ignoring traditional banner ads and disruptive marketing tactics. This has led to the rise of native advertising, a powerful and effective approach that focuses on integrating promotional content seamlessly within the user experience. Native ads aim to provide value and relevance to the audience, matching the form and function of the platform on which they appear. This non-disruptive advertising strategy fosters engagement and builds trust, ultimately leading to higher conversion rates and improved brand perception globally.
This article delves into the world of native advertising, exploring its various forms, benefits, and best practices. We will examine how sponsored content, in-feed ads, and recommendation widgets can be leveraged to reach target audiences in a more natural and engaging way. From understanding the importance of transparency and disclosure to crafting compelling narratives that resonate with users, we will provide a comprehensive guide to mastering the art of native advertising and achieving exceptional results for your marketing campaigns. Prepare to discover how blending seamlessly into the user experience can unlock unparalleled opportunities for growth and brand success.
What is Native Advertising? A Comprehensive Definition
Native advertising is a form of advertising designed to seamlessly integrate into the user experience of a particular platform or website. Unlike traditional display ads, which are often disruptive and easily identifiable as advertising, native ads mimic the look and feel of the surrounding content.
The goal of native advertising is to provide valuable or engaging content that resonates with the audience, thereby increasing brand awareness and driving conversions in a less intrusive manner. This approach aims to circumvent “banner blindness” and improve the overall effectiveness of advertising campaigns.
Essentially, native advertising endeavors to blend in naturally, providing information or entertainment that aligns with the interests of the target demographic, rather than overtly promoting a product or service.
Key Characteristics of Native Advertising: Non-Disruptive and Contextual
Native advertising distinguishes itself through two pivotal characteristics: being non-disruptive and contextual. Unlike traditional advertising that often interrupts the user experience, native ads are designed to blend seamlessly into the surrounding content.
Non-disruptive nature means that the advertisement doesn’t feel intrusive or jarring. It respects the user’s journey and avoids aggressive tactics. This is achieved by mirroring the format, style, and tone of the platform or website on which it appears. Users are therefore more likely to engage with it.
Contextuality refers to the relevance of the advertisement to the surrounding content and the user’s interests. A highly contextual native ad provides value to the user by offering information, entertainment, or solutions that are directly related to their current needs or interests. This relevance is key to driving engagement and positive brand perception.
Therefore, the success of native advertising hinges on its ability to deliver valuable content that enhances, rather than detracts from, the user experience.
Types of Native Advertising: In-Feed Ads, Content Recommendations, and More

Native advertising manifests in various forms, each designed to integrate smoothly within a specific platform’s user experience. Understanding these types is crucial for effective campaign deployment.
In-Feed Ads
These ads appear directly within the regular content stream of a website or social media platform. They mimic the look and feel of organic posts, making them less intrusive. Examples include promoted posts on Facebook or sponsored articles on news websites.
Content Recommendations
Often found at the bottom of articles, these ads suggest related content that users might find interesting. They are designed to blend with the site’s recommendations engine, appearing as genuine suggestions rather than overt advertisements.
Paid Search Ads
While seemingly distinct, paid search ads are a form of native advertising. They appear in search engine results pages (SERPs) and are designed to match the user’s search query, blending seamlessly with organic results.
Promoted Listings
Common on e-commerce sites and marketplaces, promoted listings are ads that appear within the regular product listings. They are typically marked as “sponsored” or “promoted” but maintain the same visual style as organic listings.
Benefits of Native Advertising: Increased Engagement and Brand Awareness
Native advertising offers a multitude of benefits, primarily centered around enhanced user engagement and heightened brand awareness. Its non-disruptive nature allows it to seamlessly integrate into the user experience, leading to a more receptive audience.
By aligning with the platform’s content and style, native ads circumvent the banner blindness often associated with traditional advertising. This increased relevance fosters a greater willingness among consumers to interact with the advertisement, thereby boosting engagement metrics such as click-through rates and time spent viewing the content.
Furthermore, the contextual relevance of native advertising contributes significantly to brand awareness. When a brand’s message is delivered within a relevant and engaging context, it resonates more strongly with the target audience. This positive association strengthens brand recall and fosters a more favorable perception of the brand, ultimately leading to increased brand recognition and affinity.
Native Advertising vs. Traditional Advertising: Key Differences
Native advertising and traditional advertising differ significantly in their approach and presentation. Traditional advertising, such as banner ads or television commercials, is often disruptive and easily identifiable as advertising.
In contrast, native advertising aims to blend seamlessly with the surrounding content and user experience. This means it mimics the form and function of the platform on which it appears, making it less intrusive and more likely to be viewed as valuable content.
Here’s a brief comparison:
- Intrusiveness: Traditional ads are often intrusive, while native ads are designed to be non-disruptive.
- Appearance: Traditional ads are clearly identifiable as advertisements, while native ads resemble the surrounding editorial content.
- User Experience: Traditional ads can detract from the user experience, while native ads aim to enhance it.
- Control: Traditional ads often allow for more creative control, while native ads require adherence to platform guidelines for form and function.
Examples of Successful Native Advertising Campaigns
Examining successful native advertising campaigns reveals the power of seamless integration and contextual relevance. These examples demonstrate how brands can connect with audiences without disruption.
Netflix and The Wall Street Journal
Netflix partnered with The Wall Street Journal to create a native ad article exploring the economics of incarceration, aligning with the themes present in their original series, “Orange is the New Black.” This well-researched and thought-provoking piece generated significant engagement.
GE and The New York Times
General Electric (GE) collaborated with The New York Times to produce a series of sponsored articles and interactive features showcasing their innovations in science and technology. The “4D-Printed Metal Engine Parts” campaign, for instance, highlighted GE’s cutting-edge work in a visually engaging and informative manner. This demonstrated subject matter expertise and company thought leadership.
IKEA and Facebook
IKEA ran a native advertising campaign on Facebook, showcasing its products within a lifestyle context. The ads featured short, engaging videos of people using IKEA furniture in their homes, illustrating the practicality and style of the brand’s offerings.
The Importance of Disclosure in Native Advertising
Disclosure is paramount in native advertising to maintain trust and transparency with consumers. Because native ads are designed to blend seamlessly with the surrounding content, it’s crucial that users can clearly distinguish between editorial content and paid advertising.
Failure to properly disclose native advertising can lead to deceptive practices, eroding consumer trust and potentially resulting in legal repercussions. Regulatory bodies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) emphasize the need for clear and conspicuous disclosures.
Acceptable disclosure methods include using labels such as “Sponsored,” “Advertisement,” or “Promoted” placed prominently near the native ad. The language used should be easily understood by the average consumer, avoiding vague or ambiguous terminology.
Ultimately, transparent disclosure protects both consumers and advertisers. It allows consumers to make informed decisions about the content they are engaging with, while building long-term credibility and trust for brands utilizing native advertising strategies.
Native Advertising Platforms and Networks
To effectively implement native advertising campaigns, marketers often leverage specialized platforms and networks. These platforms connect advertisers with publishers, streamlining the process of creating, distributing, and managing native ads.
Several prominent native advertising platforms exist, each offering unique features and targeting capabilities. Examples include:
- Sharethrough: Known for its focus on in-feed native video ads.
- Taboola: A content discovery platform that recommends articles and videos to users.
- Outbrain: Similar to Taboola, specializing in content recommendations across a network of publisher sites.
- TripleLift: Provides a programmatic native advertising exchange.
These platforms offer various targeting options, including demographic, interest-based, and contextual targeting, allowing advertisers to reach their desired audience. They also provide tools for tracking campaign performance and optimizing ad creatives.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Native Advertising Campaigns
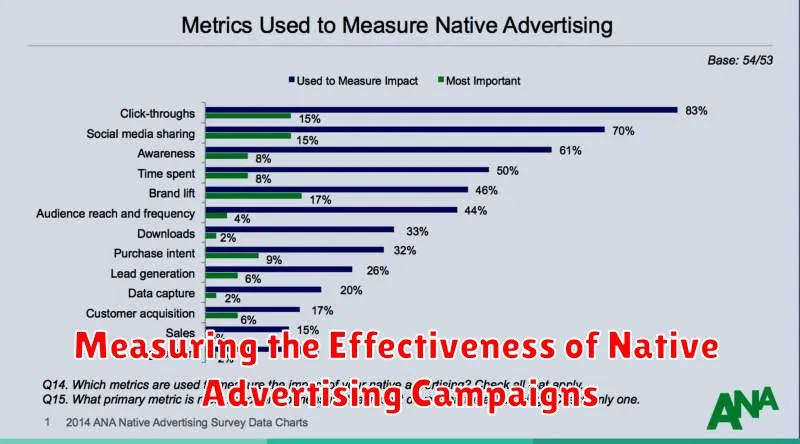
Determining the success of native advertising requires a strategic approach focusing on relevant key performance indicators (KPIs). Unlike traditional advertising metrics, native advertising effectiveness is often gauged by its ability to integrate seamlessly and drive engagement without disrupting the user experience.
Key Metrics to Track
Essential metrics include:
- Engagement Rate: Measures interactions such as likes, shares, and comments on the native ad content.
- Time Spent: Indicates how long users are engaging with the ad, reflecting its interest and relevance.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Tracks the percentage of users clicking through to the advertiser’s website or landing page.
- Conversion Rate: Monitors the percentage of users completing a desired action, such as a purchase or sign-up, after interacting with the native ad.
- Brand Lift: Assesses changes in brand perception, awareness, and favorability resulting from the native advertising campaign.
Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques can aid in measuring effectiveness, including:
- Web Analytics Platforms: Utilize tools like Google Analytics to track website traffic and user behavior.
- Social Media Analytics: Employ platform-specific analytics to monitor engagement on social media native ads.
- A/B Testing: Experiment with different ad creatives and placements to optimize performance.
The Future of Native Advertising: Trends and Predictions
The landscape of native advertising is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology and shifts in consumer behavior. Several key trends are poised to shape its future.
Firstly, we anticipate a greater emphasis on personalization. Advertisers will leverage data and AI to deliver highly targeted and relevant native ads, enhancing user engagement and ROI.
Secondly, the rise of video and interactive content will continue to impact native advertising. These formats offer richer storytelling opportunities and provide users with more immersive experiences. Expect to see more native video ads integrated into social media feeds and news articles.
Thirdly, transparency will remain paramount. Consumers are increasingly discerning, and clear disclosure of sponsored content is crucial for maintaining trust and credibility. Regulations surrounding native advertising disclosure are likely to become stricter.
Finally, the integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies into native advertising is on the horizon, offering exciting possibilities for creating deeply engaging and immersive experiences.